PAGE A:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0
Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>Untitled</title>
</head>
<body>
<cfquery datasource="data"
name="getdata">
SELECT * FROM Members
</cfquery>
<cfoutput query="getdata">
<a href="member_edit.cfm?member_id=#id#">#id#</a>,
#firstname#, #lastname#, #age#, #address1#, #address2#,
#dob#
<a
href="member_delete_submit.cfm?member_id=#id#"> Delete
</a><br>
</cfoutput>
<br>
<a href="member_add.cfm">ADD
Record</a><br>
</body>
</html>
Notes: The HTML above produces the figure above. The numbers on the left side of the query
data are used to link the user to another page where updates are
performed. The tag <a
href="member_edit.cfm?member_id=#id#">#id#</a>, is used to accomplish the link to the
member_edit.cfm page, passing a
variable (member_id) to that page. The
number are values from the field named ID in the Access Data.
The tag <a
href="member_delete_submit.cfm?member_id=#id#"> Delete </a>
work simular to the before mention tag.
The difference is the link to the page called
member_delete_submit.cfm. Notice that
an member_id is being past. This is
used to locate the record you wish to delete.
The tag <a href="member_add.cfm">ADD
Record</a> create a submit button, labeled “Add Record” to allow the user
to add records to the database. No
member_id needs to be past since we are creating a new record.
PAGE B:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0
Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>Add
(SQL)</title>
</head>
<h2>Add Record</h2>
<body>
<form action="member_edit_submit.cfm"
method="post">
Enter Field Values You Wish To Add:<br>
<br>
First Name: <input type="Text"
name="firstname" size=30 value><br>
Last Name: <input type="text"
name="lastname" size=30><br>
Age: <input type="text" name="age"
size=3><br>
Address: <input type="text"
name="address1" size=50><br>
Address: <input type="text"
name="address2" size=50><br>
State: <input type="text"
name="state" size=2><br>
Date Of Birth: <input type="text"
name="dob" size=12><br>
<!--<input type="hidden"
name="dob_date">-->
<br>
<br>
<input type="Submit" value="Add
Record">
</form>
</body>
</html>
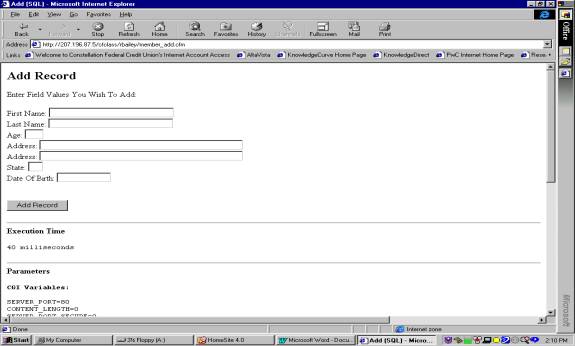
Notes:
The above HTML creates this web page. Please make sure the </form> is at the
bottom of the page, after your final submit button, not at the end of the line with
tage <form> on it. This
mistake took me hours to figure out.
And I did not get it until Micheal helped me out.
When the Add Record button is pressed the tage <form
action="member_add_submit.cfm" method="post"> calls the
member_add_submit.cfm page. All
variables created on the calling page
can be used on the page called.
PAGE: C
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0
Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>Untitled</title>
</head>
<body>
<CFQUERY Datasource = "data" Name="AddMember">
INSERT INTO Members (FirstName, LastName, Age, Address1,
Address2, State, DOB)
VALUEs ('#firstname#',
'#lastname#',#age#,'#address1#','#address2#','#state#','#dob#')
</CFQUERY>
<cfoutput>
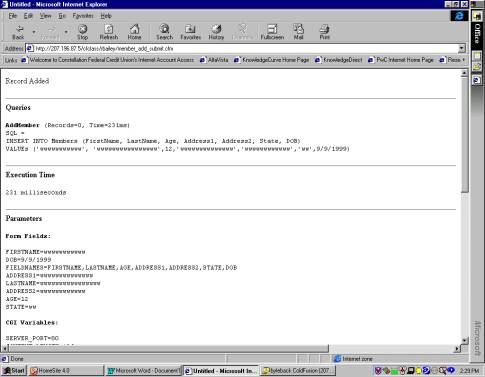
Record Added
</cfoutput>
</body>
</html>
Notes:
This is where we make our money. This is the page that submits your SQL to the datasoure
(“data”). The <CFQUERY Datasource =
"data" Name="AddMember"> defines the datasource and
labels the query with the name “AddMember”.
The INSERT statement is the standard insert statement that you can read about the Access (copy of
statement provide below). The
<CFOUTPUT> outputs to the screen “Records Add”, so that the user will
know that some kind of action has taken place.
PAGE D:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0
Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>Edit
(SQL)</title>
</head>
<h2>Edit Record</h2>
<body>
<form action="member_edit_submit.cfm"
method="post">
<cfquery datasource="data"
name="editrecord">
SELECT * FROM Members WHERE ID = #member_id#
</cfquery>
<cfoutput query="editrecord">
<input type="hidden" name="member_id"
value=#member_id#>
First Name: <input type="Text"
name="firstname" size=30 value=#firstname#><br>
Last Name: <input type="text"
name="lastname" size=30 value=#lastname#><br>
Age: <input type="text" name="age"
size=3 value=#age#><br>
Address: <input type="text"
name="address1" size=50 value=#address1#><br>
Address: <input type="text"
name="address2" size=50 value=#address2#><br>
State: <input type="text"
name="state" size=2 value=#state#><br>
Date Of Birth: <input type="text"
name="dob" size=12 value=#dob#><br>
</cfoutput>
<br>
<br>
<input type="Submit" value="Update
Record">
</form>
</body>
</html>
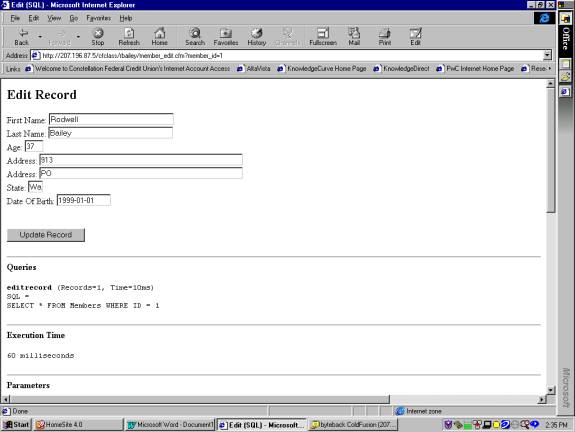
Notes:
The Edit Record screen works like the Add Record
screen. The thing to notice here is that when the number is
selected the Edit Record screen is populated with the values of the record
selected. This is accomplished by the
executing a query before the page is shown using the following code:
<cfquery
datasource="data" name="editrecord">
SELECT * FROM Members WHERE ID =
#member_id#
</cfquery>
Remember from the first screen the member_ id was past to
this screen like so:
<a
href="member_edit.cfm?member_id=#member_id#">#id#</a>
PAGE E:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>Update
(SQL)</title>
</head>
<h2>Update Record</h2>
<body>
<CFQUERY Datasource = "data"
Name="updatemember">
UPDATE Members SET
FirstName
= '#firstname#',
LastName
= '#lastname#',
Age =
#age#,
Address1
= '#address1#',
Address2
= '#address2#',
State =
'#state#',
DOB =
#dob#
WHERE ID = #member_id#
</CFQUERY>
<cfoutput>
Record Updated
</cfoutput>
</body>
</html>
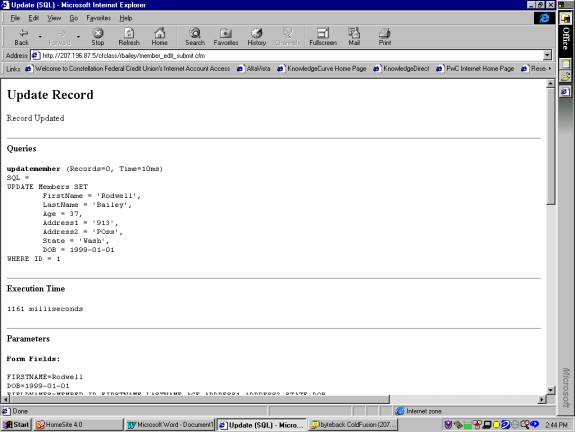
Notes:
Same as the Add page but instead of an INSERT an UPDATE is
being perforned.
PAGE F:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0
Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>Delete
Recod</title>
</head>
<body>
<CFQUERY Datasource = "data"
Name="deleterecord">
DELETE * FROM Members WHERE ID = #member_id#
</CFQUERY>
<cfoutput>
Record Deleted
</cfoutput>
</body>
</html>
Notes:
If you have gotten
this far and have understood whats been going on then you will see that this is
simular to the rest. <CFQUERY
Datasource = “data”
Name=”deleterecord”> is naming
and labeling your data source and the delete statement the same
DELETE (copy provided below) statement
in Access. Remember the member_id is
being past in to the query form the other form
ADDITIONAL NOTES:
INSERT
Adds a record or multiple records to a table. This is
referred to as an append query.
Syntax
Multiple-record append query:
INSERT INTO target [IN externaldatabase] [(field1[, field2[,
...]])]
SELECT [source.]field1[, field2[, ...]
FROM tableexpression
Single-record append query:
INSERT INTO target [(field1[, field2[, ...]])]
VALUES (value1[, value2[, ...])
The INSERT INTO statement has these parts:
Part Description
target The name of
the table or query to append records to.
externaldatabase The
path to an external database. For a description of the path, see the IN clause.
source The name of
the table or query to copy records from.
field1, field2 Names
of the fields to append data to, if following a target argument, or the names
of fields to obtain data from, if following a source argument.
tableexpression The name of the table or tables from which
records are inserted. This argument can be a single table name or a compound
resulting from an INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, or RIGHT JOIN operation or a saved
query.
value1, value2 The
values to insert into the specific fields of the new record. Each value is
inserted into the field that corresponds to the value's position in the list:
value1 is inserted into field1 of the new record, value2 into field2, and so
on. You must separate values with a comma, and enclose text fields in quotation
marks (' ').
UPDATE
Creates an update query that changes values in fields in a
specified table based on specified criteria.
Syntax
UPDATE table
SET newvalue
WHERE criteria;
The UPDATE statement has these parts:
Part Description
table The name of
the table containing the data you want to modify.
newvalue An
expression that determines the value to be inserted into a particular field in
the updated records.
criteria An
expression that determines which records will be updated. Only records that
satisfy the expression are updated.
DELETE
Creates a delete query that removes records from one or more
of the tables listed in the FROM clause that satisfy the WHERE clause.
Syntax
DELETE [table.*]
FROM table
WHERE criteria
The DELETE statement has these parts:
Part Description
table The
optional name of the table from which records are deleted.
table The name of
the table from which records are deleted.
criteria An
expression that determines which records to delete.



